Medically reviewed by Rosanna Sutherby, PharmD on January 10, 2020. Written by Kathryn Wall. To give you technically accurate, evidence-based information, content published on the Everlywell blog is reviewed by credentialed professionals with expertise in medical and bioscience fields.
Table of contents
- What Causes Yellow Skin (Jaundice)?
- Health Conditions Related to Yellow-Looking Skin
- Seeking Medical Care for Yellow-Looking Skin
- Preventing Jaundice
- Common Questions About Yellow-Looking Skin/Jaundice
- Related Content
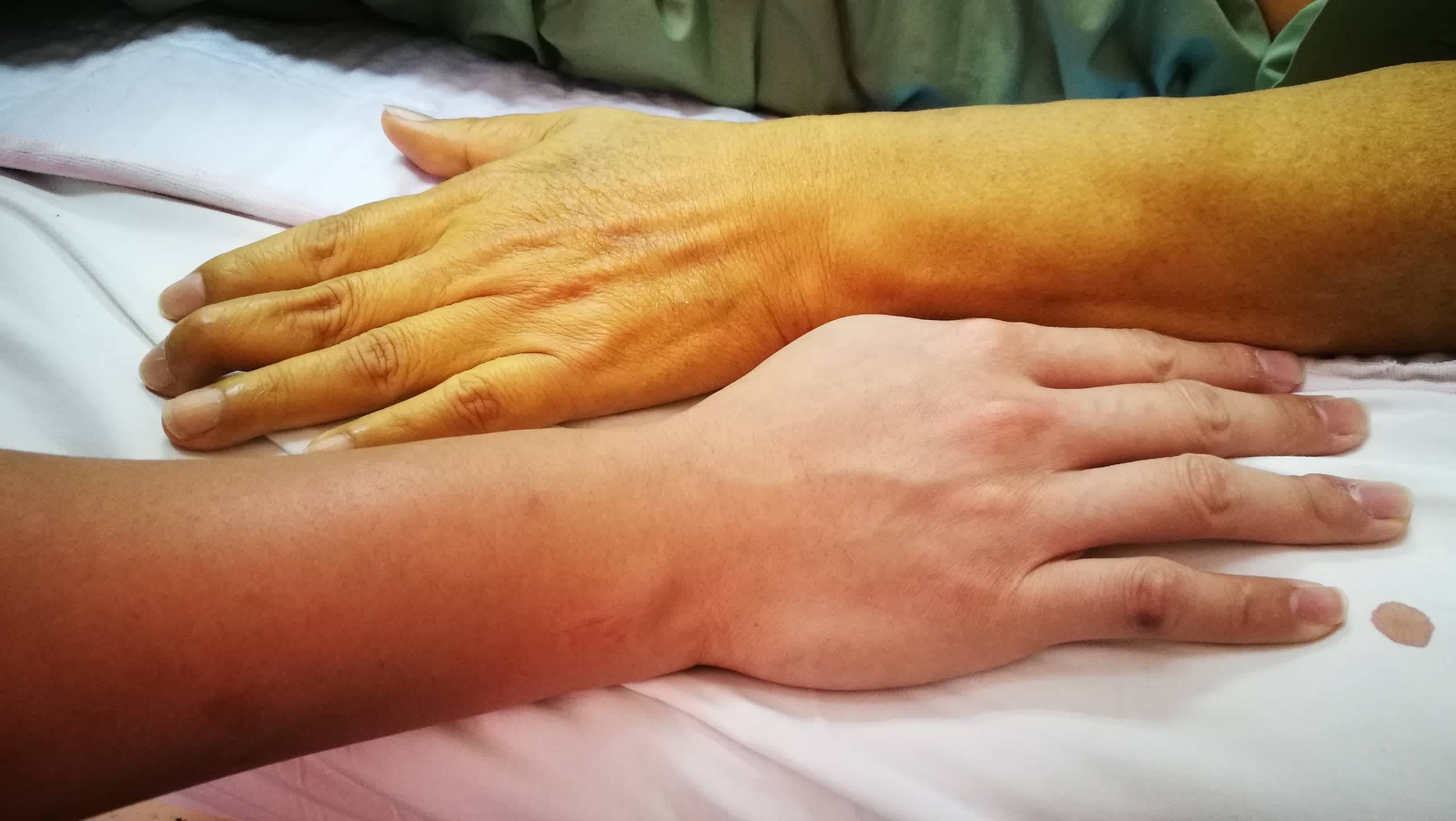
Concerned because you've noticed yellow skin around the eyes—and the skin throughout the rest of your body has taken on an abnormal yellow tint, as well?
Yellowing of the skin and/or the whites of the eyes is a classic sign of jaundice—a condition that can occur when there's a buildup of a certain natural pigment (bilirubin) in the bloodstream. If you suspect jaundice may be affecting you, read on to discover more—including possible causes, related health conditions, prevention tips, and more. (And don't forget to discuss your symptoms with your healthcare provider as soon as possible.)
What Causes Yellow Skin (Jaundice)?
Jaundice is directly caused by high bilirubin levels in the body. Bilirubin, a yellow-orange pigment in the bloodstream, primarily forms when aged red blood cells are broken down. Normally, the liver filters bilirubin from the bloodstream and moves it into the digestive tract where it is then eliminated in stool and urine.
However, when the liver isn't functioning properly—or if bilirubin production significantly increases for some reason—this substance builds up in the bloodstream and can cause a yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Other signs and symptoms of high bilirubin levels may include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Abdominal pain
- Flu-like symptoms
- Dark-colored urine
- Light-colored stool
A number of factors can lead to higher-than-normal levels of bilirubin, resulting in jaundice—such as the following.
B12 Vitamin Deficiency
Vitamin B12 plays an important role in the development of red blood cells. This essential B vitamin can be obtained through meat, poultry, eggs, and nutritional supplements. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to low levels of healthy red blood cells, leading to a type of anemia called pernicious anemia. Symptoms of pernicious anemia may include diarrhea, loss of appetite, and jaundice.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B occurs when someone is infected by the hepatitis B virus—which can damage the liver if it isn't treated promptly. The hepatitis B virus can be transmitted through body fluids such as semen and blood during activities like sexual intercourse and needle-sharing. Joint pain, dark urine, and jaundice are all symptoms of hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C occurs when someone is infected by the hepatitis C virus. Hepatitis C can cause serious harm to the liver over time and is characterized by many of the same symptoms of hepatitis B—including nausea, vomiting, and jaundice. Estimates suggest that about 1 in 5 cases of acute hepatitis C results in jaundice.
Certain Medications
Certain drugs and medications like painkillers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anabolic steroids, birth control pills, and statins can hurt the liver and cause jaundice. Liver damage that occurs as a result of these medications is called drug-induced liver injury, which is characterized by symptoms including dark urine, fever, and jaundice.
Bile Duct Obstruction
Before bilirubin is eliminated from the body, it moves through the bile duct into the digestive tract. Blockage in the bile duct can cause bilirubin to build up in the bloodstream, which can result in yellow skin discoloration. In many cases, blockages in the bile duct are caused by a gallstone, but some may be caused by cancer tumors or rare liver disorders. Surgery is one of the most common treatments for bile duct obstruction.
Heavy Alcohol Consumption
The liver is responsible for breaking down alcohol in the body. However, drinking high amounts of alcohol on a regular basis can overload the liver, ultimately causing liver damage and liver disease. When the liver becomes damaged, it may have difficulty filtering bilirubin from the bloodstream—and jaundice may develop.
Health Conditions Related to Yellow-Looking Skin
Alcoholic Liver Disease
People who have been drinking heavily for many years are at higher risk of developing alcoholic liver disease. Over time, alcohol abuse can worsen liver function and contribute to high bilirubin levels, abdominal pain, and yellow skin on the hands and the rest of the body.
Gallstones and Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer is a possible complication of gallstones—hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in the gallbladder as a result of a high-cholesterol, high-fat diet, or high levels of bilirubin. Excess bilirubin contributes to the formation of gallstones, which can block the bile duct, preventing bilirubin from exiting the body.
Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is caused by long-term damage and scarring of the liver due to alcohol abuse, hepatitis B and C, autoimmune diseases of the liver, or other factors. Common symptoms of liver cancer include abdominal pain, an enlarged abdomen, unexplained weight loss, and jaundice. Treatment options for liver cancer can include surgery or liver transplantation.
Seeking Medical Care for Yellow-Looking Skin
If you notice that your skin is turning yellow or you develop a yellow tinge in the whites of the eyes, see your healthcare provider as soon as possible to receive a proper diagnosis. A healthcare professional may help identify the root cause of your jaundice and start a treatment regimen, if necessary. To determine the cause of jaundice, laboratory tests (such as liver function tests), imaging tests, and/or a liver biopsy may be recommended.
Seek medical attention right away if you're experiencing any of the following symptoms with jaundice:
- Blood in vomit
- Stools that are tarry, black, or bloody
- Severe pain or tenderness in the abdomen
- Fever
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Agitation
- Bruising or bleeding easily
The above symptoms may indicate a serious medical condition that requires immediate treatment.
Preventing Jaundice
Steps you can take that may help prevent jaundice include:
-
Eating a well-balanced, nutrient-rich diet that provides adequate amounts of vitamin B12 (and if you aren't able to get enough B12 from your diet, consider taking a B12 supplement regularly; Everlywell also offers a B6 vitamin supplement option)
-
Avoiding toxins that can injure liver cells such as cigarette smoke
-
Consume only low to moderate amounts of alcohol
-
Talk with your healthcare provider about any medications you're on that can contribute to liver damage—and learn what their recommendation is for you
-
Use medications responsibly, and don't mix them with alcohol or other substances that can lead to liver toxicity
-
Get vaccinated for hepatitis B
-
Test for hepatitis C to learn your status (you can easily do this from the privacy of home with the Everlywell at-home Hepatitis C Test). Note that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that all adults age 18+ get tested for hepatitis C at least once.
Common Questions About Yellow-Looking Skin/Jaundice
Why Do I Have a Yellow Spot on My Skin?
Yellowing of the skin—whether it's one spot or an all-over discoloration—may be an indication of jaundice. It could be due to something else, however. So the best course of action to take if you notice a yellow spot on your skin? See your healthcare provider as soon as possible, as they can help determine what the cause is.
Could I Have Liver Disease Without Jaundice?
Though jaundice may be one of the most common signs of liver disease, it's possible to have liver disease with delayed jaundice or without jaundice. Other symptoms of liver disease may include fatigue, weakness, fever, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, light-colored stool, and pain under the right side of the ribs.
Related Content
How Much Vitamin B12 Should I Take Daily?
7 Signs of Hepatitis C To Be Aware Of
References
- Kalakonda A, Jenkins BA, John S. Physiology, Bilirubin. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470290/. Accessed January 10, 2020.
- Stillman AE. Jaundice. In: Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW, editors. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd edition. Boston: Butterworths; 1990. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK413/. Accessed January 10, 2020.
- Pernicious anemia. MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000569.htm. Accessed January 10, 2020.
- Hepatitis B. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/viral-hepatitis/hepatitis-b. Accessed January 10, 2020.
- Hepatitis C. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/viral-hepatitis/hepatitis-c. Accessed January 10, 2020.
- Lohia P, Jinjuvadia R, May E. Profound jaundice in a patient with acute hepatitis C. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013200233. Published 2013 Sep 12. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-200233
- Testing Recommendations for Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hcv/guidelinesc.htm. Accessed January 10, 2020.
- Drug-induced liver injury. MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000226.htm. Accessed January 10, 2020.
- Maher JJ. Exploring alcohol's effects on liver function. Alcohol Health Res World. 1997;21(1):5-12.
- Gallstones. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gallstones/symptoms-causes/syc-20354214. Accessed January 10, 2020.
- Liver cancer - hepatocellular carcinoma. MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000280.htm. Accessed January 10, 2020.
- 13 Ways to a Healthy Liver. American Liver Foundation. https://liverfoundation.org/13-ways-to-a-healthy-liver/. Accessed January 10, 2020.
- Symptoms of liver disease. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. https://www.hepatitis.va.gov/basics/liver-disease-symptoms.asp. Accessed January 10, 2020.
Spotlight on
Featured content

86% of cancers aren't caught by recommended screenings. See what they're missing with a single blood draw.
Save $100 now
Explore Everlywell








